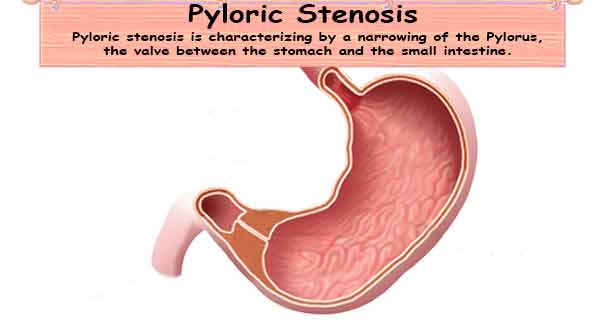
What is pyloric stenosis? Pyloric stenosis is characterizing by a narrowing of the pylorus, the opening from the stomach into the small intestine.
What is pyloric stenosis?
Pyloric stenosis is a condition characterizing by a narrowing of the opening (pylorus sphincter) from the stomach to the first part (duodenum) of the small intestine due to enlargement of the muscle surrounding pylorus. This causes spasms when the stomach empties.
In pyloric stenosis, it is unsure whether there is a congenital narrowing or functional hypertrophy of the pyloric sphincter muscle.
Newborn or infant pyloric stenosis – pyloric stenosis is a condition usually develops in male babies in the first two to six weeks.
Congenital pyloric stenosis – is generally infant hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. It presents with vomiting starting after the second week of birth, suggests it has acquired.
Adults Pyloric Stenosis - Pyloric stenosis is more commonly diagnosing among infants; however, it is also developing among adults. In adults, the cause is generally narrowing of pylorus due to a scar tissue from a nearby chronic peptic ulceration.
Pyloric stenosis affects both boys and girls; however, boys are four times more chances to have this condition. It is most often occurred around the second or third week of birth also may develop at any time up to the age six months.